Understanding Diabetes
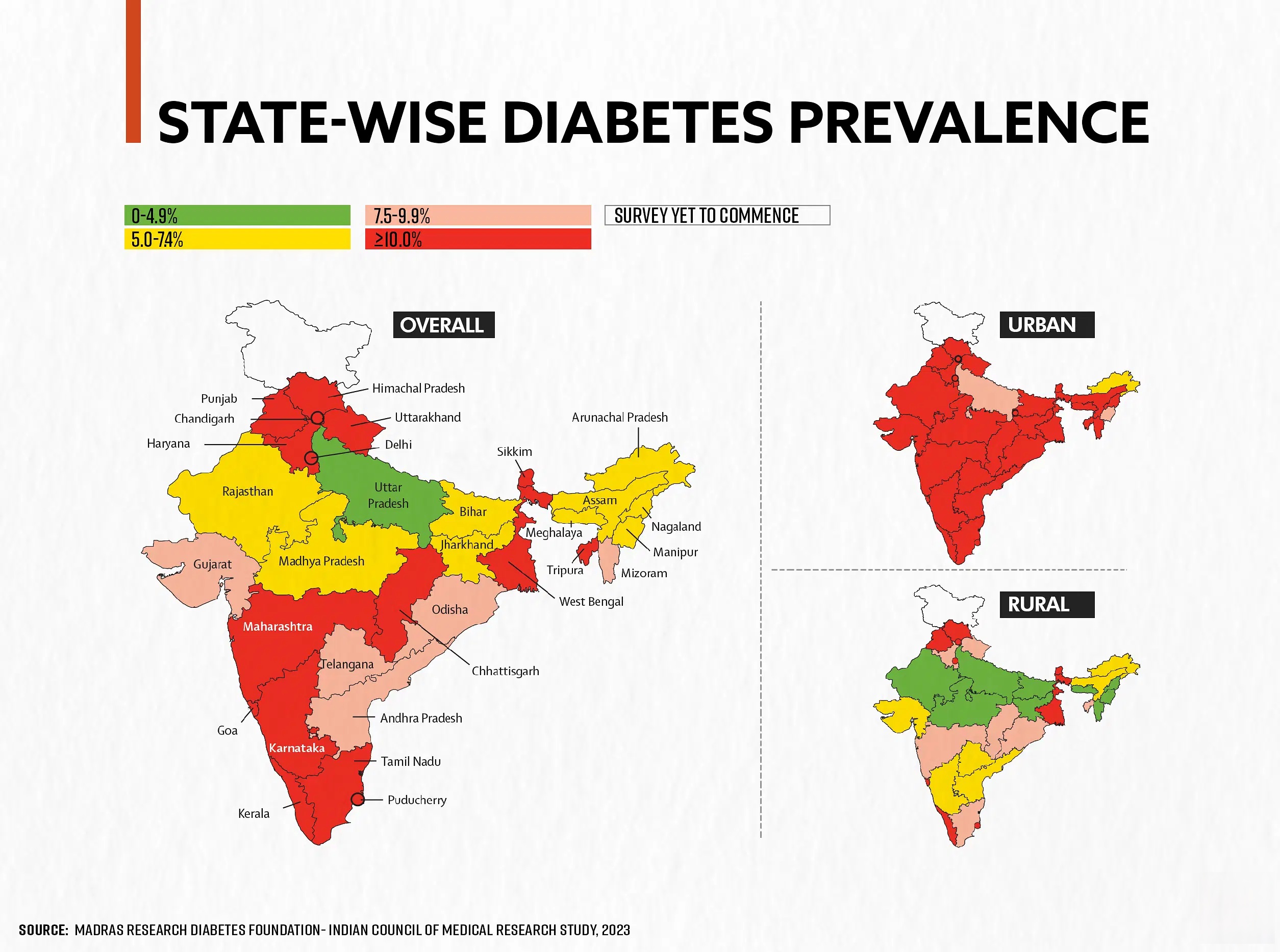
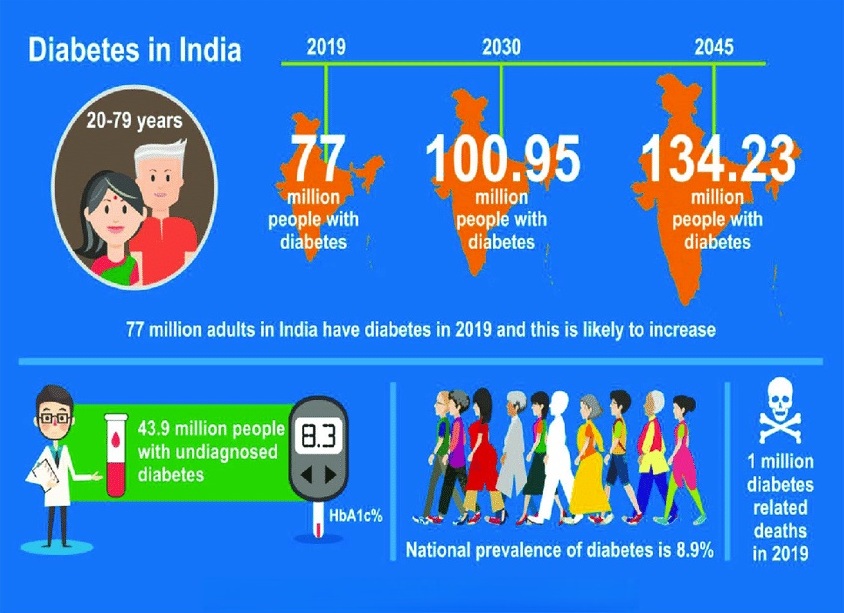
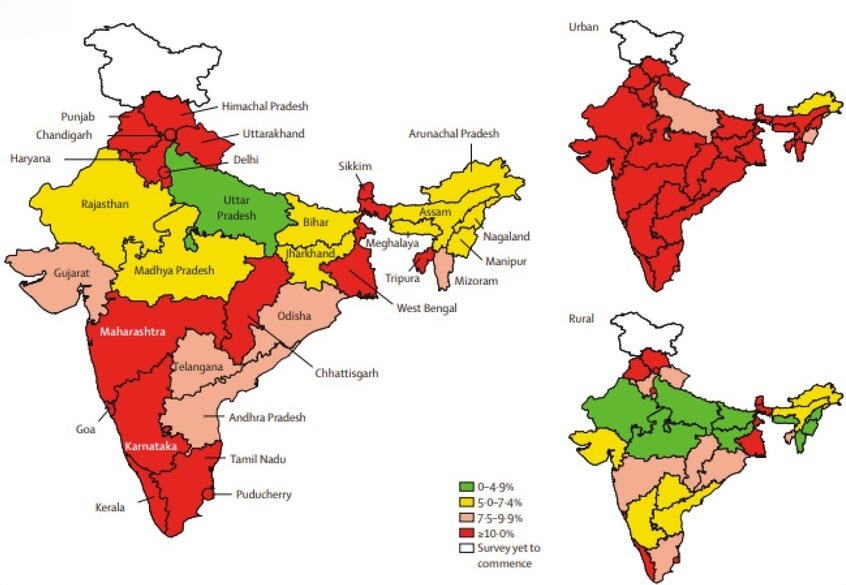
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose (or blood sugar), which over time leads to serious damage to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. India is home to the second-largest population of people with diabetes in the world, with over 77 million adults currently living with the condition. The prevalence of diabetes in India has been rising rapidly due to urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy diets, and genetic predisposition.
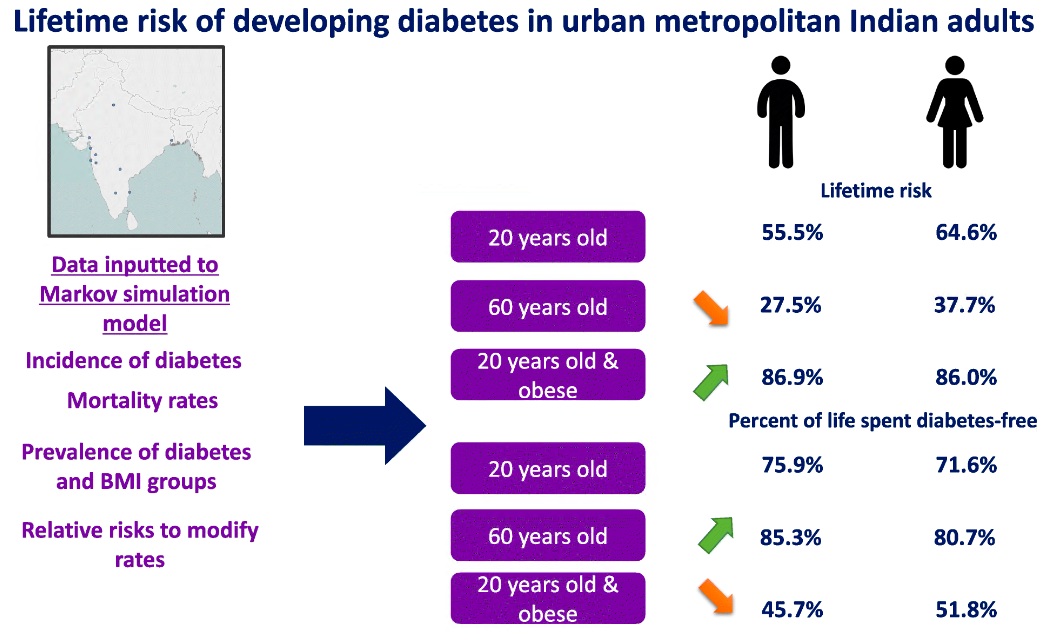
There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 2 diabetes is far more common in India, accounting for over 90% of all cases. Type 2 diabetes is largely preventable and manageable through lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, maintaining a normal body weight, and avoiding tobacco use.
The economic burden of diabetes in India is significant, affecting not only individuals but also families and the healthcare system. Early diagnosis and effective management are crucial to prevent complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, blindness, and lower limb amputation.
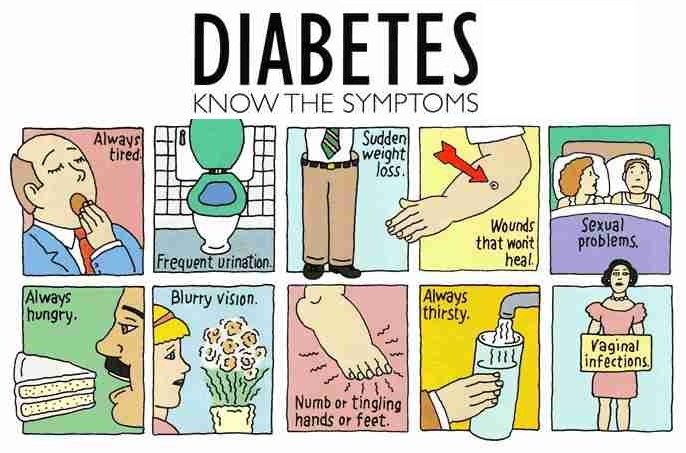
Symptoms of Diabetes
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme hunger
- Sudden vision changes
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
- Feeling very tired much of the time
- Very dry skin
- Sores that are slow to heal
- More infections than usual
Prevention and Management
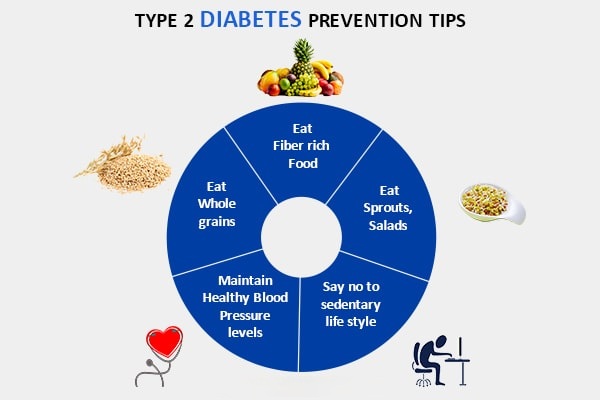
Prevention of diabetes, especially Type 2, is possible through:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Engaging in regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes per week)
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption
- Regular health check-ups and blood sugar monitoring
What My Clients Say
Raj M. 25 - Bengaluru, Karnataka
Meera Z. 36 - Chennai, Tamil Nadu
Ayesha P. 63 - Mumbai, Maharashtra
Videos on Diabetes
Diabetes in India: Statistics and Challenges
According to the International Diabetes Federation, the number of adults with diabetes in India is expected to rise to 101 million by 2030. The challenges in India include lack of awareness, limited access to healthcare in rural areas, high out-of-pocket expenses, and cultural factors that influence diet and lifestyle. Government initiatives such as the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) aim to address these issues through screening, awareness, and management programs.